Creating your store
The heart of the TypeScript integration with Easy Peasy are the typing definitions you define to represent your store's model. This typing information can then be used by the various Easy Peasy APIs to provide you with assertions, code completions, etc.
For this tutorial we will create a model consisting of two slices; todos and an audit log.
Interface declaration
We will start by defining the state for our model - without actions/thunks/etc.
// The interface representing our Todos model
interface TodosModel {
items: string[];
}
// The interface representing our Audit model
interface AuditModel {
log: string[];
}
// The interface representing our entire store model
interface StoreModel {
todos: TodosModel;
audit: AuditModel;
}
Model implementation
Using our model interfaces we can create our model implementation.
const todosModel: TodosModel = {
items: []
};
const auditModel: AuditModel = {
logs: []
};
const storeModel: StoreModel = {
todos: todosModel,
audit: auditModel
}
Good ol' TypeScript will make sure that we implement the model in full.
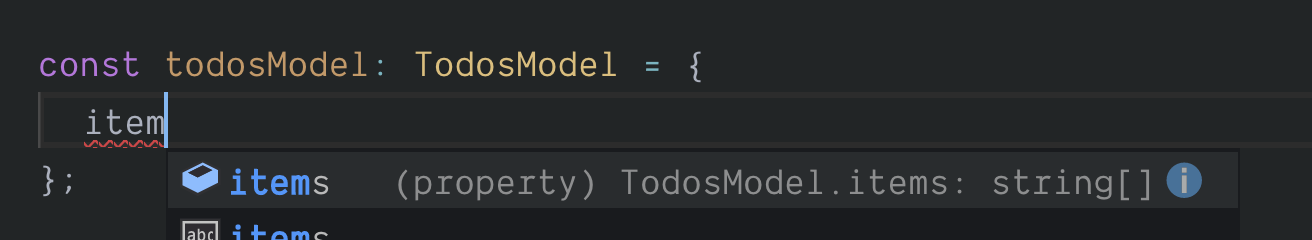 TypeScript powered model implementation
TypeScript powered model implementationFile structure
You can organise your model interfaces and implementations as you please. My personal preference is to split them out into seperate files based on slice/feature.
// todos.ts
export interface TodosModel {
items: Todo[];
}
const todosModel: TodosModel = {
items: []
};
export default todosModel;
Creating the store
Now that we have our model defined we can pass it to createStore in order to create our store.
import storeModel from './model';
const store = createStore(storeModel);
The store that is returned will be fully typed. If you try to use the store's APIs you will note the typing information and code completion being offered by your IDE.
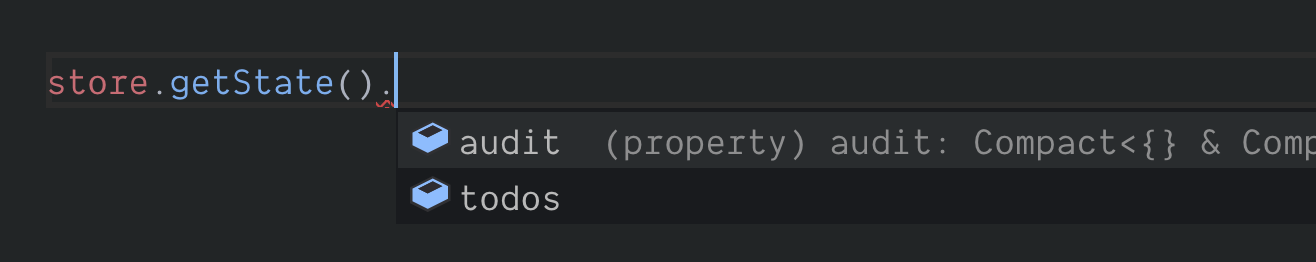 Typed store APIs
Typed store APIsReview
You can view the progress of our demo application here.